
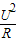 ,R=
,R=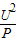 求出灯泡的电阻.
求出灯泡的电阻.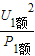 =
=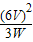 =12Ω,R2=
=12Ω,R2=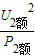 =
=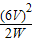 =18Ω;
=18Ω;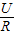 =
=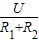 =
=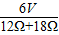 =0.2A,
=0.2A,

 名校练考卷期末冲刺卷系列答案
名校练考卷期末冲刺卷系列答案科目:初中物理 来源: 题型:
查看答案和解析>>
科目:初中物理 来源: 题型:
查看答案和解析>>
科目:初中物理 来源: 题型:
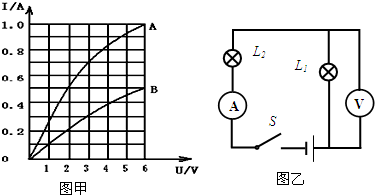
 (2010?东城区二模)小明利用标有“6V 6W”的灯L,和“6V 3W”的灯L2进行实验图中OA和OB分别为通过灯Ll和L2中的电流随其两端电压变化关系的曲线.现将两灯串联接到某电源上,其中一个灯恰好正常发光时,电路在5min内产生的热量是
(2010?东城区二模)小明利用标有“6V 6W”的灯L,和“6V 3W”的灯L2进行实验图中OA和OB分别为通过灯Ll和L2中的电流随其两端电压变化关系的曲线.现将两灯串联接到某电源上,其中一个灯恰好正常发光时,电路在5min内产生的热量是查看答案和解析>>
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com