
阅读下列文章完成任务。
Live Music-Late Night Jazz
Enjoy real American Jazz(爵士乐)from Herbie Davis, the famous trumpet player(号手).He is known to play well into the early hours, so don’t want to get much sleep.
PLACE:The Jazz Club DATES:15-23 June
PRICE:¥160 TIME:10 p. m. till late
TEL:4858749
Scottish Dancing
Scottish dancing is nice and easy to learn.The wonderful dance from England will be given.
PLACE:Jack Stein’s DATES:10-20 May
PRICE:¥160 TIME:10 a. m.-10 p. m.
TEL:4983084
Shows-Haikou Museum
There are 12 000 pieces on show here.You can see the whole of Chinese history.
PLACE:Haikou Museum DATES:30 Mar.-30 June
PRICE:¥60(half for students)
TIME:Mon.-Fri.9 a. m.-5 p. m.
Weekends 9 a. m.-9 p. m.
TEL:4467834
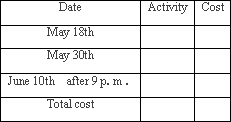
Your friend will come and stay with you from May 15th to June 15th.Finish the Activity table for her using the information above.
 天天向上一本好卷系列答案
天天向上一本好卷系列答案 小学生10分钟应用题系列答案
小学生10分钟应用题系列答案科目:高中英语 来源: 题型:阅读理解
任务型阅读 (共10小题; 每小题1分,满分10分)
请认真阅读下列短文,并根据短文的内容要点完成文章后的表格列单。
注意:补全填空应符合语法和搭配要求,每格只填一个单词。
Even British People Can’t Speak English Properly
There are different regional accents across the UK, and a number of regions have several different dialects, that is, they have their own unique vocabulary and grammatical phrases. There were at least six different accents born to London the last time I counted.
Worse than that, it is not just where a person is born in the UK that decides their accent. For example, a language and its accents often vary across class or level of education. Another example is how language can differ among age groups in the UK. The words and pronunciations used by young people in the UK can be radically different compared with those used by adults.
Yoof culture
The word ‘yoof’ is a slang spelling of ‘youth’. Some people consider ‘yoof’ to be a negative term, since its pronunciation is easier and lazier than ‘youth’. Other people see the term as positive, because it describes how young people are creating their own language, concepts and identity. When people find it difficult to understand their children, the children can say more things than without censorship(审查,检查) of their parents. In this way, young people are starting to find freedom, independence and self-expression. They are creating a ‘yoof culture’.
It is not possible to come up with a complete list of words used by yoof. By the time the list was completed, it would be out of date. New words come and go like fashions. However, a few features of the yoof style of language are as follows:
◆instead of saying something like ‘That’s good!’ or ‘I understand’, yoof will use a single adjective like ‘Safe!’, ‘Sorted!’, ‘Sound!’, ‘Cool!’ or ‘Wicked!’.
◆instead of ‘He then said no!’, yoof will say ‘She was like: no!’
◆Instead of ‘She’s attractive!’, yoof will say ‘She’s fine!’ or ‘She’s fit!’
◆Instead of ‘I don’t care!’, a yoof will say ‘Whatever!’.
New social and political language
Certain groups of society feel threatened by ‘yoof culture’ or by the British working classes having more social freedom. As a result, a negative term now commonly used in the UK is ‘chav’. It is insult and is meant to describe someone who is uneducated and anti-social (e.g. ‘He’s a chav!’). A young person who wears a jacket with a hood(风帽,头巾) (after all, it rains a lot in the UK) is sometimes called a ‘hoodie’. It is a negative term and suggests that the young person is interested in committing crime.
Where does that leave us?
Learners of English often feel that the best test of their English is how well they can talk to a native speaker. Yet learners should not worry about communicating with native speakers so much. Research conducted by the British Council shows that 94 per cent of the English spoken in the world today is spoken between non-native speakers of the language. In fact, when we think about ‘international English’, there is no such thing as native or non-native speakers. The UK no longer owns the English language.
 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||