
第9讲
一、Language points

 1. when 既可指时间的某一点,从句中的谓语动词可以是非延续性的,又可指一段时间(从句中的谓语动词要用延续性动词),从句的动作与主句的动作同时发生。
1. when 既可指时间的某一点,从句中的谓语动词可以是非延续性的,又可指一段时间(从句中的谓语动词要用延续性动词),从句的动作与主句的动作同时发生。
意为“这时”,常用结构:be about to…when…
as: 强调从句的动作和主句的动作同时发生,而不是一前一后。
while: 表示两者情况对比。
 2.
be of +抽象名词=be + adj.
2.
be of +抽象名词=be + adj.
be of (great) + use/help/value/importance
=be (very) + useful/helpful/valuable/important
 3.
journey:适用范围广,可指陆海空的旅行,常指距离较远的旅行。
3.
journey:适用范围广,可指陆海空的旅行,常指距离较远的旅行。
trip:指短时间,短距离的旅行。
travel:泛指旅游,前面一般不用冠词。
travels:多指旅行经历
journey和trip强调往返性,travel不侧重往返性,可以是章程旅行。
Voyage:海上旅行或航海。
 4. hope:指与过去、现在或将来有关的希望,不能接名词,双宾语或复合宾语。
4. hope:指与过去、现在或将来有关的希望,不能接名词,双宾语或复合宾语。
 wish:多指美好的祝愿,或表达的是过去,现在或将来发生的令人遗憾的事,接从句时使用虚拟语气。
wish:多指美好的祝愿,或表达的是过去,现在或将来发生的令人遗憾的事,接从句时使用虚拟语气。
hope for:希望、期待、对(某物)有信心
 We hope you’ll be very
happy.
We hope you’ll be very
happy.
I wish I had gone to that party.
We haven’t heard from him for a long time, but we are still hoping for a letter.
 5.
n.诺言,有指望,有前途,可能性
5.
n.诺言,有指望,有前途,可能性
There is a promise of better weather tomorrow.
keep a promise→break a promise
 promise carry out a promise:履行诺言
promise carry out a promise:履行诺言
fulfill a promise:实现诺言
v.许诺,答应,有…迹象,使…很有可能
I can’t promise, but I’ll do my best.
The clouds promise rain.
promising adj. 有前途的,有希望的
 6. put up:搭起,建筑
6. put up:搭起,建筑
set up:建立,成立
build:建造
build up:建立
found:创立,创办
 7. around/round the corner:在拐角处,即将到来
7. around/round the corner:在拐角处,即将到来
in the corner:在角落里
on the corner:在拐角上
at the corner:在拐角处(比on的范围大)
 8. sb/sth
8. sb/sth
 praise sb for (doing) sth:因…赞扬…
praise sb for (doing) sth:因…赞扬…
sb as…:称赞…是…
sing high praise for:称赞…
in praise of:赞美

 9. population:对此进行提问时,要使用what,人口的“多,少”使用large, small;表示“有多少人”时用“has
a population of…”。
9. population:对此进行提问时,要使用what,人口的“多,少”使用large, small;表示“有多少人”时用“has
a population of…”。
population:用作主语时,谓语动词的单复数由其后面的表语来决定。
 ----What’s the population
of
----What’s the population
of
----
The
population of
The population of developing countries are mostly peasants.
 10. come to terms with:达成协议,妥协
10. come to terms with:达成协议,妥协
take possessions of:获得,占有
in/with relation to:与…有关联,关于
in memory of sb:为了纪念某人
match…with…:把…和…搭配起来
二、语法专题──情态动词和虚拟语气的考点
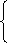 1. 表示推测:情态动词+ be+表:现在状态
1. 表示推测:情态动词+ be+表:现在状态
be doing:现在动作
have done:过去
may/might have done:本可以干某事
can/could have done:本能够干某事
should/ought to have done:本应该干某事
needn’t have done:本不必干某事
would/should like/love to have done:过去本想干某事
had better have done:当初最好干某事
would rather have done:当然真该干某事
注:情态动词表推测时,其反意疑问句,应把情态动词变为不是推测的来考虑。
2. 几个情态动词的辨析与特殊用法:
(1)can/could用于肯定句中表“可以”,或“能够”(强调与生俱来的能力);be able to强调过去设法完成的某一具体的动作。
(2)used to表示过去常常干某事,暗示“现在不干了”,以及表示过去一直存在的状态;would表示过去常常干某事,但不涉及现在的情况,还可以表示过去一直烦人的事情。
(3)need/dare作为实义动词时,应用need/dare to do; 作为情态动词时,一般不用于肯定句中。
(5)will可以表示意愿或必然趋势。
If he won’t help us, all our plans will be ruined.
The window won’t open.
(4)shall用于第一、三人称,表示征询对方意见或请求;用于第二、三人称时,表示命令、强制、允诺或威胁。
3. 虚拟语气应用于如下结构中:
(1)一种定语从句:It’s time that+did
(2)两种目的状语从句:
so that/in order that+ can/may/could/might +do
(3)三种随时变化句:
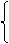
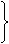 ① wish 现在→did/were
① wish 现在→did/were
if only + 过去→had done
as if/though 将来→could/would do
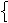 ② would rather + 现在/将来→did/were
② would rather + 现在/将来→did/were
过去→had done
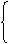 ③ 现在:if+did/were, would+ do
③ 现在:if+did/were, would+ do
过去:if+had done, would+ have done
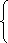 将来: did
将来: did
if+ were to do, would+ do
should do
注意:除了由if引导的虚拟条件句外,还有倒装条件句,即把were、had或should提前;混合时间句,虚实错综句,以及含蓄条件句,即由or, otherwise, with, without, but for来引导的。
(4)四种名词性从句:
①当表语是important, natural, necessary, possible, strange, arranged, decided, demanded, ordered, requested, suggested, surprising, a pity, no woder时,主语从句要用虚拟语气。例:
It’s important that we (should) help each other.
②动词一坚持(insist),两命令(command, order),三建议(advise, propose, suggest),四要求(ask, demand, request, require)后的宾语从句要用虚拟语气。例:
He insisted that he (should) be sent to the West.
注:insist(坚持说), suggest(暗示,表明)时,从句应用陈述语气。如:
Her pale face suggested that she was ill.
③idea, plan以及表示“坚持,命令,建议,要求”等动词的同源名词作主语时,表语从句用虚拟语气。例:
My suggestion is that we (should) hold a class meeting.
④idea, plan以及表示“坚持,命令,建议,要求”等动词的同源名词后的同位语从句要用虚拟语气。例:
The office gave an order that his soldiers fight back bravely.
巧用上下文语境。①注意上下文的信息提示:信息提示出现在前文时,可以根据前文的信息提示确定答案;信息提示出现在后文时,我们应该先把此空暂时搁置,在理解了后文的基础上,再确定答案。②通读全文,利用复现词语:完形填空试题中,一些词语会重复出现在语篇之中。词汇复现使得语篇中的句子相互衔接,从而构成一个完整的、有机的意义整体。把握这些反复出现的词语,有助于我们确定正确答案。
例1:
A. dictionary B. teacher C. student D. recorder
[分析]because在此引导一个原因状语从句,因为读物中使用的语言符合读者的语言水平,读者当然不必求助于词典。
例2:All of a sudden I started to feel rather__1__. She wondered why I was looking for this sort of__2___. I felt even more hopeless when she told me that it would be difficult to get a job without experience.
三、题型归纳──完形填空解题要决二
1. A. encouraged B. dissatisfied C. hopeless D. pleased
2. A. place B. job C. advice D. help
[分析]文章讲到作者去应聘工作,既没有经验又信心,心里感到十分不踏实。从下文中的“I felt even more hopeless”可知第1题填“hopeless”,暗示作者那种无望的心情。而“it would be difficult to get a job without experience”则呼应了第2题,故选job。
例3:Years ago in
A. spent B. counted C. saved D. played
[分析]分析上面一段文字可知Clark夫妇存钱的目的是让一家人出去旅游。根据文中“but they had 3(finally) saved enough money”可知第1题答案为C项。
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com