
题目列表(包括答案和解析)
When Julie was a child, she was a very big fan of animals. As a result, 36 she ever heard growing up was “Julie, you should be a vet. You’re going to be a great vet. That’s what you should do.” 37 when she got to the Ohio State University, she started studying to be a vet.
A scholarship allowed her to spend her 38 year studying abroad in Manchester, England. Away from the family 39 back home, she found herself one day sitting at her desk, surrounded by biology books and staring out the window, when it suddenly hit her: “I’m in total 40 . I don’t want to be a vet!”
41 she thought back over all the things she’d done in her life and what had made her happy. And then it hit her—it was all of the youth leadership conferences that she had volunteered 42 , and the communications and leadership courses she had taken as elective courses back at Ohio State. “How could I have been so 43 ? Here I am in my fourth year at school and just finally realizing I’m on the 44 path. I just never took the time to 45 it until now, ” she thought.
Inspired by her new 46 , Julie spent the rest of her year in England taking courses in communications and media studies. When 47 to Ohio State, she was eventually able to 48 the administration to let her create her own program in “leadership studies”, 49 it took her 2 years longer to finally graduate. She 50 to become a senior management consultant in leadership training and development for the Pentagon. She 51 founded a drug-prevention organization that 52 the message “Lead your own life with the skill and the 53 to say no.”
So, never live someone else’s 54 . If you limit your 55 only to what seems possible or reasonable, you disconnect yourself from what you truly want.
|
1. |
|
|
2. |
|
|
3. |
|
|
4. |
|
|
5. |
|
|
6. |
|
|
7. |
|
|
8. |
|
|
9. |
|
|
10. |
|
|
11. |
|
|
12. |
|
|
13. |
|
|
14. |
|
|
15. |
|
|
16. |
|
|
17. |
|
|
18. |
|
|
19. |
|
|
20. |
|
请认真阅读下面短文,从短文后各题所给的A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出最佳选项,并在答题卡上将该项涂黑。
People do not analyze every problem they meet.Sometimes they try to remember a solution from the last time they had a 36 problem.They often accept the opinions or ideas of other people.Other times they begin to act without 37 ; they try to find a solution by trial and error.However, when all of these methods 38 , the person with a problem has to start analyzing.There are six 39 in analyzing a problem.
First the person must recognize that there is a problem.For example, Sam’s bicycle is broken, and he cannot ride it to class as he usually does.Sam must 40 that there is a problem with his bicycle.
Next the person must 41 the problem.Before Sam can repair his bicycle, he must know why it does not work.For example, he must 42 the parts that are wrong.
Now the person must look for 43 that will make the problem clearer and lead to 44 . solutions.For example, suppose Sam 45 that his bike does not work because there is something wrong with the brakes.At this time, he can look in his bicycle repair book and read about brakes, talk to his friends at the bike shop, or look at his brakes carefully.
After 46 the problem, the person should have 47 suggestions for a possible solution.Take Sam as an example 48 , his suggestions might be: tighten or loosen the brakes, buy new brakes and change the old ones.
In the end, one 49 seems to be the solution 50 the problem.Sometimes the 51 idea comes quite 52 because the thinker suddenly sees something new or sees something in a 53 way.Sam, for example, suddenly sees there is a piece of chewing gum stuck to a brake.He immediately hits on the solution to his problem: he must 54 the brake.
Finally the solution is 55 .Sam does it and finds his bicycle works perfectly.In short, he has solved the problem.
36.A.serious B.usual C.similar D.common
37.A.practising B.thinking C.understanding D.helping
38.A.fail B.work C.change D.develop
39.A.ways B.conditions C.stages D.orders
40.A.explain B.prove C.show D.see
41.A.judge B.find C.describe D.face
42.A.check B.determine C.correct D.recover
43.A.answers B.skills C.explanation D.information
44.A.possible B.exact C.real D.special
45.A.hopes B.argues C.decides D.suggests
46.A.discussing B.settling down C.comparing with D.studying
47.A.exact B.enough C.several D.countless
48.A.once B.again C.also D.alone
49.A.suggestion B.conclusion C.decision D.discovery
50.A.with B.into C.for D.to
51.A.next B.clear C.final D.new
52.A.unexpectedly B.late C.clearly D.often
53.A.simple B.different C.quick D.sudden
54.A.clean B.separate C.loosen D.remove
55.A.recorded B.completed C.tested D.accepted
请认真阅读下面短文,从短文后各题所给的A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出最佳选项,并在答题卡上将该项涂黑。
People do not analyze every problem they meet. Sometimes they try to remember a solution from the last time they had a 36 problem. They often accept the opinions or ideas of other people. Other times they begin to act without 37 ; they try to find a solution by trial and error. However, when all of these methods 38 , the person with a problem has to start analyzing. There are six 39 in analyzing a problem.
First the person must recognize that there is a problem. For example, Sam’s bicycle is broken, and he cannot ride it to class as he usually does. Sam must 40 that there is a problem with his bicycle.
Next the person must 41 the problem. Before Sam can repair his bicycle, he must know why it does not work. For example, he must 42 the parts that are wrong.
Now the person must look for 43 that will make the problem clearer and lead to 44 . solutions. For example, suppose Sam 45 that his bike does not work because there is something wrong with the brakes. At this time, he can look in his bicycle repair book and read about brakes, talk to his friends at the bike shop, or look at his brakes carefully.
After 46 the problem, the person should have 47 suggestions for a possible solution. Take Sam as an example 48 , his suggestions might be: tighten or loosen the brakes, buy new brakes and change the old ones.
In the end, one 49 seems to be the solution 50 the problem. Sometimes the 51 idea comes quite 52 because the thinker suddenly sees something new or sees something in a 53 way. Sam, for example, suddenly sees there is a piece of chewing gum stuck to a brake. He immediately hits on the solution to his problem: he must 54 the brake.
Finally the solution is 55 . Sam does it and finds his bicycle works perfectly. In short, he has solved the problem.
| 36.A.serious 37.A.practising 38.A.fail 39.A.ways 40.A.explain 41.A.judge 42.A.check 43.A.answers 44.A.possible 45.A.hopes 46.A.discussing 47.A.exact 48.A.once 49.A.suggestion 50.A.with 51.A.next 52.A.unexpectedly 53.A.simple 54.A.clean 55.A.recorded | B.usual B.thinking B.work B.conditions B.prove B.find B.determine B.skills B.exact B.argues B.settling down B.enough B.again B.conclusion B.into B.clear B.late B.different B.separate B.completed | C.similar C.understanding C.change C.stages C.show C.describe C.correct C.explanation C.real C.decides C.comparing with C.several C.also C.decision C.for C.final C.clearly C.quick C.loosen C.tested | D.common D.helping D.develop D.orders D.see D.face D.recover D.information D.special D.suggests D.studying D.countless D.alone D.discovery D.to D.new D.often D.sudden D.remove D.accepted |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
阅读下面短文,掌握其大意,然后从短文后所给各题的四个选项(A、B、C和D)中,选出可以填入空白处的最佳选项,并在答题卡上将该项涂黑。
People do not analyse every problem they meet.Sometimes they try to remember a solution from the last time they had a 1problem.They often accept the opinion or ideas of other people.Other times they begin to act without 2; they try to find a solution by trial and error.However, when all of these methods 3, the person with a problem has to start analyzing .There are six 4in analysing a problem.
5, the person must recognize that there is a problem.For example, Sam’s bicycle is broken, and he cannot ride it to class as he usually does.Sam must 6that there is a problem with his bicycle.
Next the person must 7the problem.Before Sam can repair his bicycle, he must know why it does not work.For example, he must 8the parts that are wrong.
Now the person must look for 9that will make the problem clearer and lead to 10solutions.For example, suppose Sam 11that his bike does not work because there is something wrong with the brakes.12, he can look in his bicycle repair book and read about brakes, talk to his friends at the bike shop, or look at his brakes carefully.
After 13the problem, the person should have several suggestions for a possible solution.Take Sam as an example 14, his suggestions might be: tighten or loosen the brakes; buy new brakes and change the old ones.
In the end, one 15seems to be the solution to the problem.Sometimes the 16idea comes quite 17because the thinker suddenly sees something in a 18way.Sam, for example, suddenly sees there is a piece of chewing gum stuck to a brake.He immediately hits on the solution to his problem: he must 19the brake.
Finally the solution is 20.Sam does it and finds his bicycle works perfectly.In short he has solved the problem.
1.A.serious B.usual C.similar D.common
2.A.practice B.thinking C.understanding D.help
3.A.fail B.work C. change D.develop
4.A.ways B.conditions C.stages D.orders
5.A.First B.Usually C.In general D.Most importantly
6.A.explain B.prove C.show D.see
7.A.judge B.find 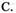 describe D.face
describe D.face
8.A.check B.determine C.correct D.recover
9.A.answers B.skills C.explanation D.information
10.A.possible B.exact C.real D.special
11.A.hopes B.argues C.decides D.suggests
12.A.In other words B.Once in a while C.First of all D.At this time
13.A.discussing B.settling down C.comparing with D.studying
14.A.secondly B.again C.also D.alone
15.A.suggestion B.conclusion C.decision D.discovery
16.A.next B.clear C.final D.new
17.A.unexpectedly B.late C.clearly D.often
18.A.simple B.different C.quick D.sudden
19.A.clean B.separate C.loosen D.remove
20.A.recorded B.completed C.tested D.accepted
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com