
0.4 99.9% $3.98
2. 句号――英语中最普通的终止号,它标志着除感叹句、直接疑问句以外的所有句子的结束。主要用于:
(1) 陈述句和祈使句后。
Honesty is the best policy. Be sure to get here on time.
(2) 用于间接疑问句。
He asked us where we got the money.
(3) 用于缩写词后。
Mr. Jones Dr. Richards St. Nick Ph. D. Oct. etc.
(4) 用在小数的数字中。
1. 逗号――英语中最小的停顿。主要用于:
(1)逗号和并列连词and, but, or, nor, for, so等一起用来连接两个独立分句。
We didn’t know the address, but we had their telephone number.
We must go now, or it will be late.
(2) 逗号用在引导性的介词短语、分词、ing形式、不定式和从句之后。
When the sun went down, we started the fire.
In the middle of the room, there is a big Christmas tree. Exhausted, she fell asleep on the chair.
(3) 逗号用于分隔非限制性句子成分。
For most foreigners, who have no knowledge of English, language is the chief problem.
Shakespeare’s tragedy, Macbeth, is one of his greatest plays.
(4) 逗号用在一系列结构平行的句子成分中。
He speaks slowly, clearly, and emphatically. I studied English, French, and Latin.
(5) 逗号用于分隔插入成分、过渡词语和对照词语。
The picnic, it seems, will be held on Sunday.
You, too, may have a try. The problem, however, remains unsolved.
(6) 逗号用来分隔感叹句、呼语词和反意疑问句中的附加疑问句。
Goodness, did the bell ring? Excuse me, sir, is this a bank? You will not leave, will?
(7) 逗号用来分隔句子的修饰语(独立成分)。
Considering the weather, we made a good time.
Generally speaking, women are more careful than men.
(8) 逗号用来把yes, no与句子的其它部分分开。
Yes, he is. No, I don’t.
(9) 逗号用于分隔日期、地点、地址、数字、书信、头衔、直接引语等。
She graduated on July 6, 1996, from Beijing University.
He lives in St. Louis, Missouri.
1,918,102
Dear John,
Jerry Smith, M.A., Ph. D.
She said, “Only a fool would believe you.”
(10) 为避免误解、明确句子意思而必须时,用逗号。
As far as I can ~, the result has not been promising.
Whatever is, is right.
After he broke his hand, writing was very difficult for him.
2. 规范三写
单词或字母的大小写、拼写和书写达到规范化。
(1)考生要把字母写得易于辨认,尤其是a, o;u, r, v;e, t, c;h, l等在手写体中易于混淆的字母,一定要写清楚。
(2)应特别注意英语文章标题中的大小写的写法,一般来说实词、拼写较长的介词的首字母要大写,简单做法可以有只大写标题的首单词的首字母,其余均小写;另外有些学生会将小写s占格为大写,这也是要杜绝的。
(3)干净整洁的卷面可以打动阅卷老师的心,有可能获得意外的高分。
高考书面表达评分细则规定,评分时“要考虑标点符号的准确性。”英语的标点符号和汉语的标点符号有相似之处,但也有不同之点。尤其是英语中的逗号、句号和分号与汉语的用法不甚相同。
1. 移行的规则
移行应遵循单词的音节。音节的划分一般为“一归后,二分手,字母组合手拉手”。
“一归后”:指两个元音字母之间有一个辅音字母时,在移行划分音节时,这个辅音字母归后,如:student→ stu-dent, definite→ de-fi-nite。
“二分手”:指两个元音字母之间有两个辅音字母时,在移行划分音节时要分属前后。如:supper→ sup-per, middle→ mid-dle, compound→ com-pound。
“字母组合手拉手”:指凡是固定字母组合的发音移行时不可分开,如:picture, national中的ure, tion不能拆开。
以下细节问题更要注意:
(1)一个字母构成的音节,不能在它的前后拆开移行,如ahead, idea不能拆成a-head, i-dea。
(2)单音节词不论其长短都不能拆开移行,如:text, horse, straight。
(3)带有铅坠或后缀的词移行时,应在前缀与词根相接处拆开移行,如:careful→ care-ful, boyhood→ boy-hood。
(4)复合词移行时,应在连字符处或构成的两部分之间拆开。如:bookstore→ book-store, headmaster→ head-master。
(5)有些动词的简略式不可拆开移行,如:aren’t, don’t, haven’t, shouldn’t等。
(6)词尾-ed,-es等中的e不发音第 1 页 共 1 页时,就不算一个音节,不能拆开移行,如:walked, stayed, goes。
材料二:起源于美国的金融风暴袭击欧洲,影响全球。目前甲岛(图10所示)所在国人a约32万,人均负债43.2万美元。
(1)甲岛名称为_。金融危机造成该岛所在国粮食供应更加紧张,简析其粮食不足的自然原因。(4分)
(2)乙岛位于甲岛的_方向;按岛屿成因划分,乙岛应属于_岛。试分析乙岛降水分布的特点及其成因。(6分)
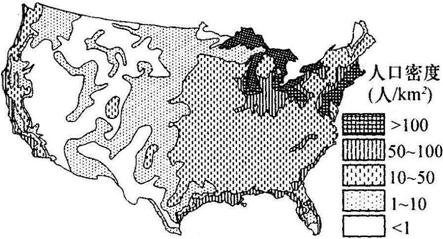
(1)根据材料一简述美国人口 空间分布特点,并分析东北大西洋沿岸和五大湖区人口密度大的主要原因。(6分)
(2)美国是世界上农业最发达的国家之一,其农业发展条件优越。与我国相比,美国发展农业的自然条件的优势有哪些?(4分)
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com