
1.生物体中的化学元素
3. 教育价值:
(1) 理解自然界一切物质包括生物体都是由化学元素组成的,不存在特殊的“生命元素”。
(2) 了解生物大分子的种类和作用,为后续学习奠定基础。
(3) 学会生化检测方法,并初步学习如何探究。
4 修改说明
根据新的课程标准,该章内容为原教材(实验本)中第二章的一部分。编写组根据试验阶段反馈的情况,将“生物组织中某些化合物的分析”实验进行了修改,分为生化检测技术的学习(必做)和应用技术检测营养成(选做)分两部分。在完成课程标准要求的基础上,让有条件的学校强化实验技术和应用的训练。
5 修改纲要
第1节 生物体中的化学元素(1,1+0)
关键问题 生物体是由哪些元素组成的
2. 学习过程:
(1)通过对人和玉米的主要化学元素组成的比较,了解组成生物体的元素;理解组成生物体的元素在自然界中都能找到,来自于自然界;这些元素在动、植物体内的组成和含量是有差异的。
(2)通过对实验例子的分析,了解大量元素、微量元素、必需元素和非必需元素的含义。
(3)了解生物体内化合物的种类和作用,理解何为营养成份。
(4)学会用生物化学的方法检测生物大分子,并应用所学的实验方法对部分饮料、食品的营养成分进行鉴定。
(5)在校园网上建立自己班级的“生命科学”网页,并将与第1、2章相关的内容作为第一期。
1. 本章核心概念
(1) 从物质角度看生命是自然界的一个组成部分
(2) 水、无机盐、糖类、脂质、蛋白质 、核酸和维生素是生物体基本化合物
(3) 检测生物体中主要化合物的方法及其应用
2. 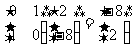
(b) Onto
which line is the line with the equation 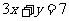 mapped under the
translation mapping
mapped under the
translation mapping  ?
?
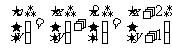
therefore,
u = x + 2 and v = y + 1
rearrange to make x and y the subject:
x = u - 2 and y = v - 1
substitute into the original equation:
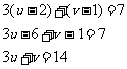
Therefore the new equation is 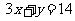 . Draw a diagram and check!
. Draw a diagram and check!
EXERCISES FOUR:
Q1. The line with the equation 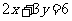 undergoes, separately, each of the following transformations:
undergoes, separately, each of the following transformations:
(a) a translation 3 units to the left parallel to the x axis followed by a dilation of factor 2 perpendicular to the x axis.
(b) reflection in the line with equation y = x followed by reflection in the x axis.
Find the equation of the image in each case.
Q2. The circle with equation 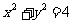 undergoes, separately each of the following transformations,
a translation
undergoes, separately each of the following transformations,
a translation  followed by a reflection in the line with the equation y =
x. Find the equation of the image.
followed by a reflection in the line with the equation y =
x. Find the equation of the image.
Q3. A parabola with the equation 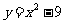 is transformed
according to
is transformed
according to
(a)  (b)
(b) 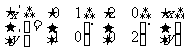
Find the equation of the image in each case and state the nature of the transformation.
Q4. The line with equation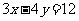 is transformed according to
is transformed according to
(a)  (b)
(b) 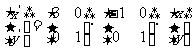 .
.
Find the equation of the image in each case and state the nature of the transformation.
SOLUTIONS
Q1. (a) 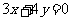 (b)
(b) 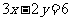
Q2. 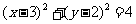
Q3. (a)  ; reflection in the x axis followed by a rotation of
90 degrees about the origin.
; reflection in the x axis followed by a rotation of
90 degrees about the origin.
(b) 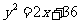 ; dilation of factor 2 parallel to the x and y
axis, followed by reflection in the line with the equation y=x.
; dilation of factor 2 parallel to the x and y
axis, followed by reflection in the line with the equation y=x.
Q4.
(a) 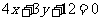 ; reflection in y = x followed by reflection in the x
axis.
; reflection in y = x followed by reflection in the x
axis.
(b)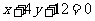 ; reflection in y axis followed by dilation of factor
3 parallel to x axis.
; reflection in y axis followed by dilation of factor
3 parallel to x axis.
1.  then
then
3. Verify each of the solutions in 2 above by using matrix multiplication, and check this by drawing the graph of the two linear relations on the same set of axes and identifying the point of intersection (using CAS).
MATRICES AND TRANSFORMATIONS OF A POINT IN A PLANE
Matrices can be used to determine the result of transformations of a point on the cartesian plane. The three types of transformations to be considered are:
· Translations
· Reflections
· Dilations
We will consider each of these in turn and also consider how the CAS can be used to determine the result of these transformations.
TRANSLATIONS
Translations have two components, movement parallel to the x-axis and movement parallel to the y-axis. The matrix for translation can be defined as:
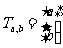
where a = movement parallel to the x-axis and b = movement parallel to the y-axis.
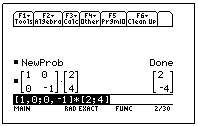
Consider the point (2, 4) that is transformed by the transformation  . This moves the point 1 unit parallel to the x-axis
and -3 units parallel to the y-axis.
. This moves the point 1 unit parallel to the x-axis
and -3 units parallel to the y-axis.
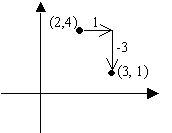
We can see that the resultant point is (3,1)
We can use this to determine the new equation of a line after it has been translated.
EXAMPLE ONE
Consider the line with the equation 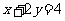 . Onto what line does it map, under the following translation
of
. Onto what line does it map, under the following translation
of  ?
?
If a point P(x, y) has an image point Q(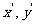 ) then under the translation
) then under the translation  ,
,
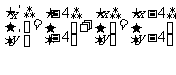
Therefore 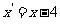 and
and 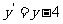 .
.
Rearranging these equations gives 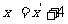 and
and 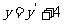 .
.
Substituting these values into the original
equation 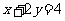 , gives
, gives

So the new equation of the translated line
is 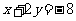
EXAMPLE TWO
Find the equation of the image curve, where  is the translation that has occurred to the parabola with the
equation
is the translation that has occurred to the parabola with the
equation 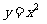 . Describe the effect of the given translation on the given
curve.
. Describe the effect of the given translation on the given
curve.
Therefore 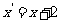 and
and 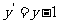 .
.
Rearranging these equations gives 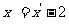 and
and 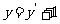 .
.
Substituting these
values in 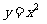 , gives:
, gives:
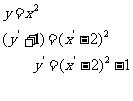
Hence the new equation is 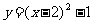 , as expected!
, as expected!
EXERCISE ONE:
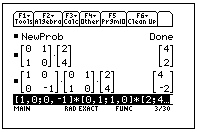
Q1. Onto what point does the translation  map each of the following points?
map each of the following points?
(a) (1, 4) (b) (2, 4) (c) (5, -3) (d) (a, b)
Q2. What translation will map the point A onto the point A in the following cases?
in the following cases?
(a) A
(4, 2) A (6, 4) (b) A(2,
-3) A
(6, 4) (b) A(2,
-3) A (4, -4) (c)
A(4, 3) A
(4, -4) (c)
A(4, 3) A (0, 0)
(0, 0)
(d) A(-3,
-1) A (-5, 3)
(-5, 3)
Q3. Consider the line
with the equation 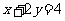 . Onto what line does it map, under the following translations?
. Onto what line does it map, under the following translations?
(a) 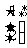 (b)
(b) 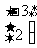 (c)
(c)

Q4. Describe the effect of the given translation on the given curve and find the equation of the image curve in each case.
(a) 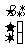 on the circle with the equation
on the circle with the equation  .
.
(b) 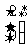 on the parabola with the equation
on the parabola with the equation 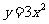 .
.
(c)  on the hyperbola with the equation
on the hyperbola with the equation 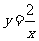 .
.
SOLUTIONS
EXERCISE ONE
Q1. (a) (3, 3) (b) (4, 3) (c) (7, -4) (d) (a+2, b-1)
Q2. (a) 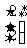 (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)
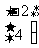
Q3. (a) 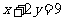 (b)
(b) 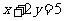 (c)
(c) 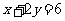
Q4. (a) circle, radius 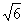 units, centre (3,
1);
units, centre (3,
1); 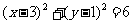
(b)
parabola, vertex at (2, 0); 
(c)
hyperbola; asymptotes y = 2 and x = 0; 
REFLECTIONS
In this section we will consider three types of reflections:
Reflections in the x-axis
If we reflect a point in the x-axis the x value of the coordinate remains unchanged but the y value is multiplied by negative 1. So (x, y) becomes (x, -y).
This can be defined as the matrix 
Similar logic can be applied to the other two reflections and this results in two further reflection matrices.
Reflection in the y-axis 
Reflection in the line y = x  Note:
this is the same effect as finding an inverse of a function where x and y
are interchanged.
Note:
this is the same effect as finding an inverse of a function where x and y
are interchanged.
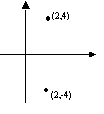
Consider our original point (2, 4).
Reflected in the x-axis: Reflected in the y-axis:

|
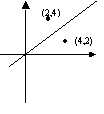

If more than one reflection occurs ensure the order is observed.
This is the point (2,4) reflected in the line y = x then reflected in the x-axis.
EXAMPLE
What does the line with
equation 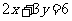 become after reflection in the
become after reflection in the
(i) x axis?
(ii) y axis?
(iii) the line with equation y = x?
(i)
Hence, 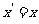 and
and 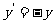
Substituting into 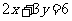 , gives
, gives 
So the equation of the reflected line is 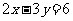
(ii)
Hence,  and
and 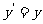
Substituting into 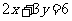 , gives
, gives 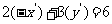
So the equation of the reflected line is 
(iii)
Hence, 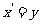 and
and 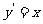
Substituting into 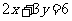 , gives
, gives 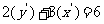
So the equation of the reflected line is 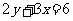
EXERCISE TWO
Q1. Write down the coordinates of the image of each of the following points after reflection in:
(i) the x axis
(ii) the y axis
(iii) the line with the equation y = x.
(a) (4, 1) (b) (3, -1)
Q2. Using matrices determine what the curve with the equation 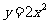 becomes after
reflection in the
becomes after
reflection in the
(i) x axis?
(ii) y axis?
Q3. Curves with equation
(a) 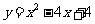 (b)
(b) 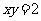
are transformed according to 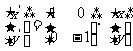 .
.
Find the equation of the image in each case.
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES TWO
Q1. (a) (4, -1); (-4, 1); (1, 4)
(b) (3, 1); (-3, -1); (-1, 3)
Q2. (i)  (ii)
(ii) 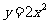
Q3. (a) 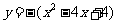 (b)
(b) 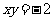
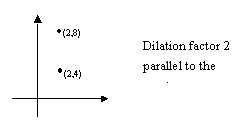
DILATIONS
We will also consider three types of dilations:
 Dilation, factor k parallel to
the y-axis
Dilation, factor k parallel to
the y-axis
|
Dilation, factor k parallel to the x-axis 
Dilation, factor k parallel to the y-axis 

|
EXAMPLE
What is the effect of a dilation by a
factor of 2 parallel to the x axis on 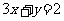 ?
?
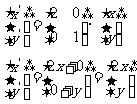
This results in the following equations : 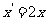 and
and 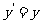 . Rearranging these equations results in
. Rearranging these equations results in 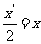 and
and 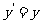 .
.
Substituting this into 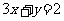 , gives:
, gives:
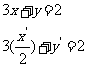
Hence the equation
of the dilated line is 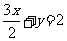
EXERCISES THREE:
Q1. What is the effect of the following dilations on the given equations?
(a)
By a factor of 3 parallel to
the y axis on 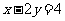 .
.
(b)
By a factor of 2 parallel to
the x axis on 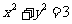 .
.
SOLUTIONS
Q1. (a) 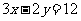
(b) ellipse 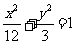
FURTHER EXAMPLES
(a) Find
the image of the point (1, -5) which has been translated by  and then
reflected in the line y = x.
and then
reflected in the line y = x.
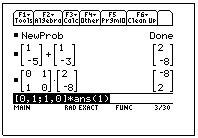
2. Write each of the following matrix equations as a pair of simultaneous equations and solve them using “by hand” skills.
(i)  (ii)
(ii) 
(二)细胞中的无机盐:1、存在形式:绝大多数以离子的形式存在,少部分是细胞内化合物的组成成分。2、功能:维持细胞和生物体的生命活动,维持细胞的酸碱平衡等。(1)是细胞的结构成分;(2)参与并维持生物体的代谢活动,如哺乳动物血液中钙盐含量过低就会出现抽搐;(3)维持生物体内的平衡:渗透压平衡(Na+、Cl-维持细胞外液渗透压,K+维持细胞内液渗透压),酸碱平衡(如人血浆中HCO3-、HPO42-等的调节)。
[思考感悟]为什么碳是最基本元素?
碳原子本身的化学性质使它能够通过化学键连接成链或环,从而形成各种生物大分子,使地球上的生命建立在碳元素的基础上。
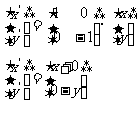
[基础训练]1、如图1是细胞中3种化合物含量的扇形图,图2是有活性的细胞中元素含量的柱形图,下列说法不正确的是( D )
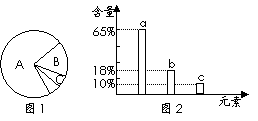 A、若图1表示正常细胞,则A、B化合物共有的元素
A、若图1表示正常细胞,则A、B化合物共有的元素
中含量最多的是a
B、若图1表示细胞完全脱水后化合物含量的扇形图,
则A化合物中含量最多的元素为图2中的b
C、若图1表示正常细胞,则B化合物具有多样性,
其必含的元素为C、H、O、N
D、图2中含量最多的元素是a,数量最多的也是a
2、分析下列材料,回答有关问题。
材料一:在正常人的血浆中,NaHCO3的含量约为H2CO3含量的20倍。当血浆中的NaHCO3含量减少时,会发生酸中毒;当血浆中的H2CO3含量减少时,则发生碱中毒。
材料二:在初生蝌蚪或幼小植物体内,当自由水的比例减小时,机体代谢强度降低;当自由水的比例增大时,机体代谢强度升高。
材料三:Mg2+是叶绿素分子必需的成分;Fe2+是血红蛋白的重要成分;碳酸钙是动物和人体的骨骼和牙齿的主要成分。
材料四:人体某些组织的含水量近似,但形态却不同。例如,心肌含水量约为79%而呈坚韧的状态,脑中含水量约为84%而呈溶胶状。
材料五:血液在血管中呈液态,当血液从血管中流出后则会凝固。
(1)材料一表明:无机盐具有调节酸碱平衡(pH)的作用。
(2)你对材料二中现象的全面解释是:自由水是细胞内良好的溶剂,是细胞内生化反应的介质,并参与某些代谢反应,参与体内营养物质和代谢废物的运输。
(3)材料三表明:无机盐是细胞内某些复杂化合物的重要组成成分。
(4)你对材料四中差异的正确解释是:组织器官的形态差异与生物体内水分的存在形式有关,心肌中结合水较多,而脑组织中自由水较多。
(5)材料五说明血液中的水分发生了怎样的转化?血液中多数自由水转化成了结合水。
3、在组成人体的各种化学元素中,最基本元素、含量最多的元素、占细胞干重最多的元素依次是( A )
A、C、O、C B、C、H、O C、C、O、N D、C、O、O
[高考模拟]4、(2006上海春考)人体中水的含量约占65%,下列选项中能正确说明水对人体重要性的是( C )
①水和糖类、蛋白质、脂肪一样,为人体提供能量;②没有水,人体内大部分化学反应就根本不会发生;③水的比热小,有利于维持体温;④体内营养物质的运输离不开水
A、①② B、②③ C、②④ D、③④
5、(2008聊城模拟)组成生物的化学元素在生物体中起重要作用。下列关于几种元素与光合作用关系的叙述中,正确的是( B )
A、C是组成糖类的基本元素,在光合作用中C元素从CO2先后经C3、C5形成(CH2O)
B、N是叶绿素的组成元素之一,没有N植物就不能进行光合作用
C、O是构成有机物的基本元素之一,光合作用制造的有机物中的氧来自于水
D、P是构成ATP的必需元素,光合作用中光反应和暗反应过程均有ATP的合成
[作业]
(一)细胞中的水:1、存在形式:自由水和结合水。2、含量:在构成细胞的各种化合物中,水的含量最多。(1)不同的生物体内水的含量差别很大;(2)同一生物体不同的生长发育阶段水的含量不同,幼儿期>成年期,幼嫩部分>老熟部分。(3)同一生物不同器官水的含量也不同。3、功能:(1)是细胞和生物体的重要组成成分;(2)是细胞内的良好溶剂,运送营养物质和代谢废物;(3)参与许多生物化学反应,如光合作用、呼吸作用等;(4)为细胞提供液体环境。4、水的含量与代谢的关系:(1)一般情况下,代谢活跃时,生物体含水量在70%以上。含水量降低,生命活动不活跃或进入休眠。(2)当自由水比例增加时,生物体代谢活跃,生长迅速。(3)当自由水向结合水转化较多时,代谢强度就会下降,抗寒、抗热、抗旱的性能提高。
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com