
2.用法:
①.表示动作在说话之前己经完成, 而后果或影响至今仍存在
a. He has gone to Shanghai. ( =He went to Shanghai and he is not here now. )
b. I have opened the window. ( =I opened the window and the window is now open.)
c. The concert has started. ( =The concert started and is now going on. )
d. I have had breakfast. (=I had breakfast and I am not hungry now. )
②.表示开始于过去, 持续到现在(也许还会继续进行下去)的动作或状态, 用于延续性动词, 且句中常带有表示段时间的时间状语
a. I have studied English since 1987.
b. He has lived here for two years.
c. He has been ill for ten days.
1.构成: have / has done
2.用法:
①.表示说话时正在进行着的动作, 或现阶段正在进行而说话时不一定正在进行的动作
a. I am writing a letter.
b. My mother is making a dress these few days.
②.表示即将发生的动作(如在最近按计划或安排好要进行的动作), 常见的有这种用法的动词有: come /go / leave / start / arrive等, 常与表示将来时间的状语连用
a. They are going to Shanghai on Friday.
b. John is coming here next week.
③.现在进行时动词与always, continually, constantly等连用, 表示反复出现的或习惯性的动作
a. The little boy is always asking questions.
b. You are always saying that sort of thing.
④.在一定的上下文中, 前一句用一般现在时动词表述现在发生的事实, 后一句用现在进行时动词来阐述这一事实的原因, 结果, 目的等
a. He frowns. He is worrying about his boy.他皱着眉头, 因为他在为他的孩子担心. (is worrying表示原因)
b. She criticizes him. She is trying to correct his wrong habits. 她批评他, 想纠正他的坏习惯. (is trying表示目的)
c. She lets her child have his own way. She is spoiling him. 她不管她的孩子, 把他惯坏了. ( is spoiling表示结果)
⑤.不表示持续的行为, 而表示知觉, 感觉, 看法, 认识, 感情, 愿望或某种状态的动词通常不用现在进行时, 如: see, hear, smell, taste, recognize, notice, forget, remember, understand, know, believe, suppose, mean, think, love, hate, care, like, dislike, worry, forgive, want, wish, hope, refuse, feel like, belong to , possess, own, have, be, seem等
1.构成: am / is / are doing
2.用法:
①.表示现状, 性质, 状态, 经常的或习惯性的动作
a. It is fine today.
b. I am a student.
c. I get up at six every day.
d. My father never takes a bus; he walks to his office.
②.表示客观事实或普遍真理
a. Japan is to the east of China.
b. The sun rises in the east.
c. A horse is a useful animal.
③.表示将来确定会发生的动作(如己安排好或计划好的动作或按时刻表将来一定会发生的动作), 可以这样使用的动词有: go, come, leave, start, arrive等
a. My train leaves at 6:30.
b. The football match is played the day after tomorrow.
④.在时间和条件状语从句中可用一般现在时动词代替一般将来时动词
a. I will let you know as soon as I hear from him.
b. We will go if it is fine tomorrow.
c. I will be away when he arrives.
d. We shall not begin the discussion until he arrives.
e. Mother, I won’t go out unless you agree.
f. Don’t try to run before you begin to walk.
⑤.在某些以here / there开头的句子中用一般现在时动词表示现在正在发生的动作
a. Here comes the bus.=The bus is coming.
b. There goes the bell.
⑥.在体育比赛过程中, 解说员叙述迅速, 短暂动作时, 可用一般现在时, 表示正在进行的或刚刚发生的动作
a. Ma Lianbao passes the ball to Mu Tiezhu, Mu shoots – a fine shot !
⑦.在剧本或图片的说明文字中, 用一般现在时表示动作
a. When the curtain rises, Juliet is sitting at her desk. The phone rings. She picks it up and listens quietly.
1.构成: 通常以动词原形表示. 主语为第三人称单数时, 则用动词的第三人称单数形式来表示
8.已知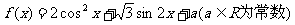
(1) 若x∈R,求f(x)的单调递增区间;
(2)
若 时,f(x)的最大值为4,求
时,f(x)的最大值为4,求 的值
的值
[解](1)由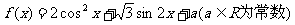
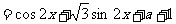
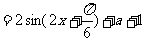 使
使
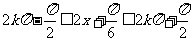 ,解得
,解得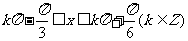 ,
,

(2)由f(x)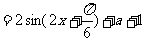 ,因此f(x)在
,因此f(x)在 上的最大值为
上的最大值为 +3,使
+3,使 +3=4,
+3=4,  =1.
=1.
6.化简

并求函数 的值域和最小正周期和递增区间.
的值域和最小正周期和递增区间.
解: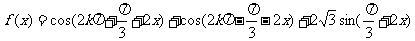
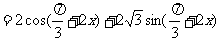

所以函数f(x)的值域为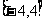 ,最小正周期
,最小正周期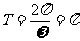
由 .(k∈Z)
.(k∈Z)
(2006上海) 求函数 的值域和最小正周期.
的值域和最小正周期.
[解] 
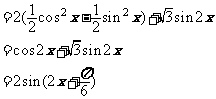
∴ 函数 的值域是
的值域是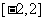 ,最小正周期是
,最小正周期是 ;
;
(2005重庆卷)若函数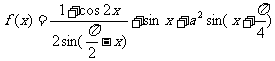 的最大值为
的最大值为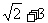 ,试确定常数a的值.
,试确定常数a的值.
解: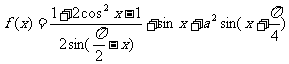
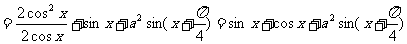

因为 的最大值为
的最大值为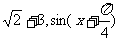 的最大值为1,则
的最大值为1,则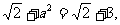
所以
19. [解](1)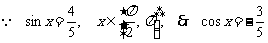 ,
,
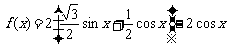

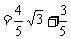 .
.
(2)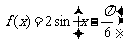 ,
,
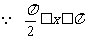 ,
, 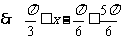 ,
, 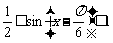 ,
,
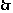 函数
函数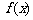 的值域为
的值域为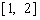 .
.
5.函数 的值域是_____________[
的值域是_____________[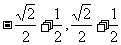 ]
]
(2006安徽)设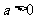 ,对于函数
,对于函数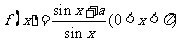 ,下列结论正确的是( )
,下列结论正确的是( )
A.有最大值而无最小值 B.有最小值而无最大值
C.有最大值且有最小值 D.既无最大值又无最小值
[例1] 试求函数y=sinx+cosx+2sinxcosx+2的最大值和最小值,若x∈[0,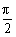 ]呢?
]呢?
剖析:注意sinx+cosx与sinx·cosx之间的关系,进行换元可将原函数转化成一元二次函数来解.
解:令t=sinx+cosx=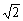 sin(x+
sin(x+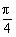 )∈[-
)∈[-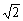 ,
,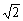 ],则y=t2+t+1∈[
],则y=t2+t+1∈[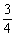 ,3+
,3+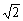 ],即最大值为3+
],即最大值为3+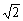 ,最小值为
,最小值为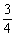 .当x∈[0,
.当x∈[0,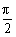 ]时,则t∈[1,
]时,则t∈[1,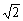 ],此时y的最大值是3+
],此时y的最大值是3+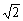 ,而最小值是3.
,而最小值是3.
评述:此题考查的是换元法,转化思想,在换元时要注意变量的取值范围.
(2006广东15)已知函数
(Ⅰ)求 的最小正周期;
的最小正周期;
(Ⅱ)求 的最大值和最小值;
的最大值和最小值;
(Ⅲ)若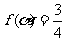 ,求
,求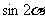 的值
的值
解: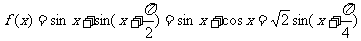
(Ⅰ) 的最小正周期为
的最小正周期为 ;
;
(Ⅱ) 的最大值为
的最大值为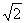 和最小值
和最小值 ;
;
(Ⅲ)因为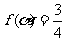 ,即
,即 ,即
,即 
(2006春上海19) 已知函数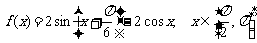 .
.
(1)若 ,求函数
,求函数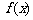 的值; (2)求函数
的值; (2)求函数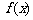 的值域.
的值域.
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com