
3. 以as,than引导的比较状语从句可全部或部分省去。
2.在虚拟条件状语从句中,如果从句中有had,should,were时,可省略if,用“had,should,were + 主语”形式。
1.当when,while,if,unless引导状语从句时,如果主从句的主语一致,且谓语部分由be动词构成(或者从句中有it is…)时,可省略主语和be动词(或省略it is)。
4.though用作副词,可位于句末,并用逗号分开。
⑦ -- Dad, I’ve finished my assignment.
-- Good, and _______ you play or watch TV, you mustn’t disturb me. (2003上海)
A. whenever B. whether C. whatever D. no matter
[考点7]before用法
注意before在下列句型中的使用
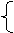 It will be + 一段时间 + before + 从句
It will be + 一段时间 + before + 从句
It won’t be long before + 从句
before一词在不同的句型中就有不同的意思,如:“在……之前”、“过了……才”、“没……就”、“不知不觉就……”等。
⑧ It will be a long time _____ Mr. Black ______ back abroad. (2002湖北八校)
A. before; comes B. since; has come
C. before; will come D. after; will come
[考点8]where引导的定语从句与where引导的地点状语从句的区别
⑨ --I have learned that a large new building will be set up ______ the Twin Towers once stood.
-- So have I. But the American people haven’t yet got over the shock of September 11.
A. where B. when C. which D. that (2004江苏南通)
[考点9]so that 可引导目的状语从句和结果状语从句
⑩ Roses need special care ________ they can live through winter. (2004全国卷)
A. because B. so that C. even if D. as
[考点10]状语从句的省略用法
3.由though或as引导的倒装句中。
2.由whether … or (not) 引导
[要点点拨]
近几年高考对状语从句的考查主要体现在以下几个方面:
[考点1]when,while与as的用法
均可表示“当……的时候”,但有区别:
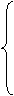 when:既可接表示动作性或短暂性的动词,也可接表示状态的动词,不强调主从句谓语动作同时发生。有时还有“这时”的意思。
when:既可接表示动作性或短暂性的动词,也可接表示状态的动词,不强调主从句谓语动作同时发生。有时还有“这时”的意思。
while:常接持续性的动词,强调主从句谓语动作同时发生,常用进行时。有时还有对比意义,意为“然而”。
as:强调同时发生或伴随进行。常用一般现在时或过去时,意为“一边……一边……”。有时还有“随着”含义。
① I do every single bit of housework ________ my husband Bob just does the dishes now and then.
A. since B. while C. when D. as (2004广西)
[考点2]“一……就……”几种表达法
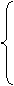 once,as soon as,the moment / minute,immediately / directly / instantly引导的从句常用一般现在时或过去时。
once,as soon as,the moment / minute,immediately / directly / instantly引导的从句常用一般现在时或过去时。
hardly / scarcely … when…和no sooner … than …结构中,前句常用过去完成式(常用部分倒装形式),后句用过去式。
On doing sth.,each / every / the first / the last + time 后也可直接接从句,一起作时间状语。
② -- Did you remember to give Mary the money you owed her?
-- Yes. I gave it to her _____ I saw her. (2004北京西城)
A. while B. the moment C. suddenly D. once
[考点3]because,as,since与for的用法比较
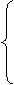 because:表示直接的原因或理由。用于回答Why的问题。because与so不能同时并列使用。
because:表示直接的原因或理由。用于回答Why的问题。because与so不能同时并列使用。
since:表示对方已知的,无须加以说明的既成事实的理由。译为“既然”。
as:表示十分明显的原因,一般说明因果关系。
for:常出现在并列句中,不说明主句行为发生的直接原因,只提供一些补充说明,且不可位于句首。
③ _______ you are leaving tomorrow, we can eat dinner together tonight. (2004江苏启东)
A. For B. Since C. When D. while
[考点4]no matter后可接who,whom,whose,which,what,when,where,how,whether
引导的让步主语从句可用whoever,whomever,whenever,whichever,whatever,wherever,
however替换,但在ever引导其它从句时不可用no matter引导。
④ _______, I have to put it away and focus my attention on study this week. (2004上海春季)
A. However the study is amusing B. No matter amusing the story is
C. However amusing the story is D. No matter how the story is amusing
[考点5]until / till的用法
⑤ It was __________ back home after the experiment. (2004湖北)
A. not until midnight did he go B. until midnight that he didn’t go
C. not until midnight that he went D. until midnight when he didn’t go
⑥ --Was his father very strict with him when he was at school?
-- Yes. He had never praised him ______ he became one of the top students in the grade.
A. after B. unless C. until D. when (2003北京春季)
[考点6]引导让步主语从句应注意等几个问题
1.由although / though , even if / though引导
注意although / though 引导从句时,主句不能用but,但可用yet或still。
34、世界文化遗产荟萃(8分)
敦煌位于今天甘肃省的西部,是内地通往西域的门户。从汉代经魏晋南北朝,到隋唐五代,通过陆上丝绸之路,中外交往频繁,敦煌因此汇聚了东西方的多种文化。规模宏大的莫高窟石窟中保存的精美壁画、雕塑,融汇了中国、印度、中亚乃至希腊文明等多种元素。1899年,在敦煌石窟中发现了大批写本残卷。这批珍贵文书被闻讯而来的英、法、俄、日等国的所谓“探险家”劫走,仅有小部分留存于国内。文献时间跨度从晋到宋,唐朝的最多,总数在四万件以上,被称为敦煌文书。其内容以佛经为主,也有大量的儒家经典、官私文书以及道教、摩尼教、基督教的经典。除了汉文文献外,还有丝绸之路上许多民族多使用语言文字写成的文献,如藏文、梵文、于阗文、粟特文等文献。敦煌文书、敦煌石窟以及相关考古发现,吸引了世界各国的学者,在20世纪形成了一门世界性的学问--敦煌学。
--摘编自白寿彝总主编《中国通史》等
(1) 根据材料并结合所学知识,概括指出敦煌学所依靠的资料。(4分)
(2) 根据材料并结合所学知识,指出敦煌学成为一门世界性学问的原因。(4分)
宁夏
12.下列关于秦朝历史的表述,不符合史实的是
 A.郡县长官均由皇帝任免
A.郡县长官均由皇帝任免
 B.太尉负责管理全国军事
B.太尉负责管理全国军事
 C.小篆以外出现了隶书
C.小篆以外出现了隶书
 D.私学也可以教授律令
D.私学也可以教授律令
 13.汉武帝时期,一位前往中国的日本人途经朝鲜半岛时可能看到
13.汉武帝时期,一位前往中国的日本人途经朝鲜半岛时可能看到
 A.作坊里正在生产麻纸
B.寺庙里在进行佛事活动
A.作坊里正在生产麻纸
B.寺庙里在进行佛事活动
 C.工匠用雕版印刷书籍
D.许多中国人在那里生活
C.工匠用雕版印刷书籍
D.许多中国人在那里生活
 14.下列不属于魏晋南北朝时期道教发展的史实是
14.下列不属于魏晋南北朝时期道教发展的史实是
 A.吸收儒家思想对道教进行改造
A.吸收儒家思想对道教进行改造
 B.吸收佛教思想以丰富道教教义
B.吸收佛教思想以丰富道教教义
 C.形成了道教主要经典《太平经》
C.形成了道教主要经典《太平经》
D.开始变成为封建统治服务的宗教
海南卷
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com